Introduction to Solar Energy and How It Works
Introduction to Solar Energy
In recent years, solar energy has rapidly gained popularity as a renewable power source, contributing to a more sustainable future for the planet. With solar panels becoming more affordable and efficient, it’s easier than ever for homeowners and businesses to harness the power of the sun. But how does solar energy work, and why should you consider adopting it? In this article, we’ll take you through the basics of solar energy, how it works, and the various types of solar power systems available today.

What is Solar Energy?
Solar energy is the energy we receive from the sun, which is harnessed through technology like solar panels. The sun’s rays are a powerful source of energy, providing more energy to the Earth in one hour than the entire world consumes in one year. Solar power harnesses this energy through photovoltaic (PV) technology or solar thermal systems, which convert sunlight into usable electricity or heat.
Solar energy is clean, renewable, and abundant, making it an excellent choice for anyone looking to reduce their carbon footprint and reliance on fossil fuels. The best part? It’s available everywhere, even in areas where traditional power sources are scarce or expensive.
How Does Solar Energy Work?
Photovoltaic (PV) Solar Panels
At the heart of solar energy systems are photovoltaic (PV) panels. These panels are made up of solar cells that convert sunlight directly into electricity. But how exactly does this conversion take place?
- Absorption of Sunlight: Solar panels are made of semiconductor materials like silicon. When sunlight hits these materials, photons (particles of light) are absorbed by the solar cells.
- Electron Movement: The absorbed energy excites the electrons in the semiconductor material, causing them to break free from their atoms and move around.
- Electricity Generation: As these free-moving electrons travel through the material, they create an electric current. This direct current (DC) electricity is captured by wiring within the solar panel.
- Inverter Conversion: Since most homes and businesses use alternating current (AC) electricity, the DC electricity generated by solar panels needs to be converted. This is where the inverter comes in—it converts the DC into usable AC electricity.
- Power Distribution: After conversion, the AC electricity is sent to the electrical panel and distributed throughout your home or business, powering lights, appliances, and other systems.
Solar Thermal Systems
While PV systems are the most common, solar thermal systems work differently by using sunlight to generate heat rather than electricity. These systems are typically used for heating water or air for residential or commercial use.
- Solar Collectors: These are devices that capture the sun’s heat. They can be mounted on roofs or other areas that receive direct sunlight.
- Heat Transfer: The collected heat is transferred via a fluid, which could be water or antifreeze. This fluid is circulated through pipes and transferred to a storage tank.
- Storage and Use: The heated fluid is stored and can be used for hot water needs, space heating, or other industrial processes. In some systems, this can significantly reduce energy costs, especially in colder climates.
Types of Solar Energy Systems
There are several types of solar systems available depending on your energy needs and location:
Grid-Tied Solar Systems
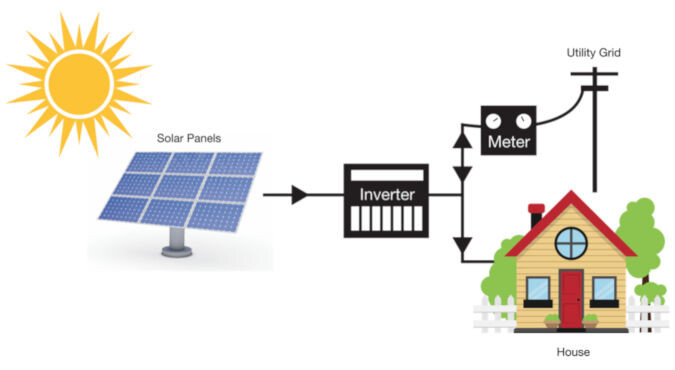
A grid-tied solar system is the most common and simplest form of solar installation. These systems are connected to the local power grid, allowing homeowners to use solar power when available and rely on the grid when the solar system isn’t producing enough energy (e.g., at night or during cloudy days).
- Benefits: It allows you to draw power from the grid, and excess solar energy can be fed back into the grid in exchange for credits or payments, known as net metering.
- Considerations: These systems require no batteries, which lowers initial installation costs but also means you have no backup power when the grid goes down.
Off-Grid Solar Systems
Off-grid solar systems are completely independent of the power grid, making them ideal for remote areas or homes looking to be fully self-sufficient. These systems use solar panels to generate electricity, and the energy is stored in batteries for use when sunlight is unavailable.
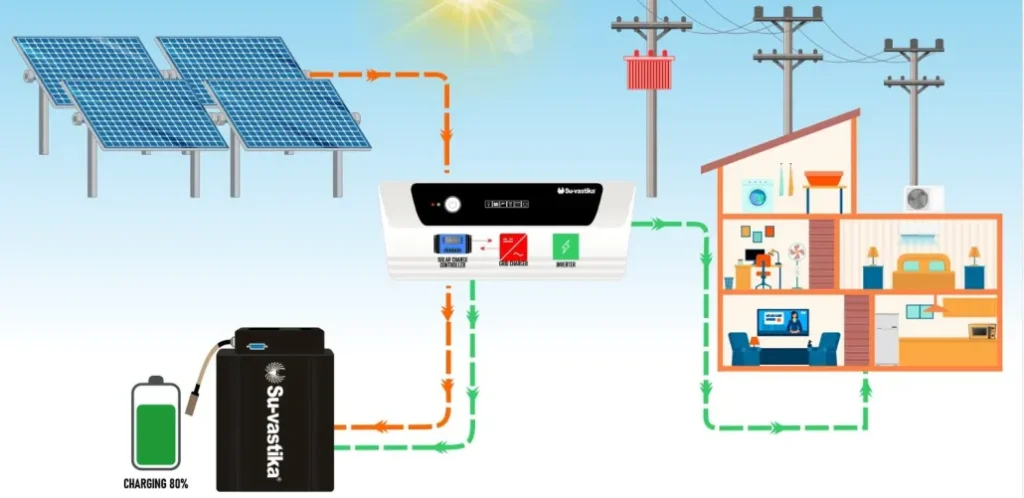
- Benefits: Off-grid systems offer complete energy independence, making them perfect for locations where grid access is unavailable.
- Considerations: They require battery storage, which adds to the cost, and the system’s capacity must be large enough to meet all the energy needs of the property.
Hybrid Solar Systems
Hybrid systems combine elements of both grid-tied and off-grid systems. These systems connect to the power grid and use battery storage to keep excess energy for use when solar power production is low.
- Benefits: A hybrid system ensures you have backup power during outages while still allowing you to sell excess power back to the grid.
- Considerations: Hybrid systems are more expensive due to the cost of batteries but offer the benefits of both grid reliance and energy independence.
Benefits of Solar Energy
Solar energy offers a range of benefits for both homeowners and businesses. These include:
- Environmental Impact: Solar energy is a clean, renewable resource that reduces carbon emissions and reliance on fossil fuels.
- Cost Savings: By producing your electricity, you can reduce or eliminate your electricity bills. In some regions, you may even receive payments for surplus energy produced.
- Energy Independence: Solar energy allows you to reduce your dependence on the grid and protect yourself from energy price fluctuations.
- Increased Property Value: Homes with solar installations tend to have higher property values, as they offer the promise of lower energy bills and increased energy independence.
- Job Creation: The solar energy industry is rapidly growing, providing thousands of jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance.
Solar Panel Efficiency
The efficiency of solar panels determines how much sunlight can be converted into usable electricity. Generally, modern solar panels are between 15-22% efficient, with high-end panels reaching efficiencies of up to 23%. Efficiency varies depending on the type of panel and its technology.
Comparison of Solar Panel Efficiency from Top Manufacturers
| Manufacturer | Efficiency (%) | Panel Type | Price Range |
| SunPower | 22.8% | Monocrystalline | High |
| LG Electronics | 21.7% | Monocrystalline | Mid-High |
| Canadian Solar | 19.9% | Polycrystalline | Affordable |
| First Solar | 17.5% | Thin-Film | Low |
For more details on the most efficient solar panels available today, refer to SunSave’s Solar Technology Guide.
Understanding Solar Tax Credits and Incentives
One of the biggest factors that can make solar energy more affordable is the availability of solar tax credits and incentives. These programs, both at the federal and state levels, can significantly reduce the upfront costs of installing solar panels.
Federal Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC)
The Federal Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC) allows homeowners and businesses to claim a tax credit of up to 30% of the total cost of installing solar panels, including panels, inverters, and installation labor. This incentive is available for solar systems installed in 2024 and beyond.
- How it works: For example, if you install a solar system worth $20,000, you can claim a $6,000 credit on your taxes. If your tax liability is lower than the credit, you can roll over the remaining amount to future years.
- Important Note: You must own the solar system to qualify. Leasing or power purchase agreements (PPAs) don’t qualify for the ITC. For a step-by-step process on how to claim this credit, check out Green Mountain Energy’s Solar Tax Savings Guide.

State and Local Incentives
In addition to the federal ITC, many states offer their incentives, such as rebates, tax credits, and low-interest loans. For example:
- California offers the Self-Generation Incentive Program (SGIP) for solar storage.
- Texas provides property tax exemptions for homes with solar panels, ensuring that their value doesn’t increase due to solar installation.
By combining federal and state incentives, you can significantly reduce the cost of your solar installation.
Conclusion
Solar energy is not only a smart choice for reducing energy bills and environmental impact, but it’s also a powerful tool for creating a sustainable future. With advancements in technology and tax incentives available, there’s never been a better time to switch to solar. Whether you’re looking to install solar panels on your home or business, understanding how solar energy works and the benefits of solar power will help you make an informed decision for a cleaner, greener tomorrow.
For a deeper dive into how solar energy is playing a key role in decarbonizing our energy systems, check out our article on Solar and Wind Energy in Decarbonizing Energy. Additionally, explore the latest innovations in solar technology by reading The Future of Solar Energy: Innovations that Will Change the World.



One thought on “Introduction to Solar Energy and How It Works”