Solar Photovoltaic Technology Its Evolution and Impact: How It Works, Types, and Future Trends
Key Takeaways
- Solar Photovoltaic Technology converts sunlight into electricity using the photovoltaic effect in semiconductor materials like silicon.
- Types of Solar Cells: There are three main types: silicon-based cells, thin-film cells, and III-V solar cells, each with varying levels of efficiency, cost, and application suitability.
- Next-Generation Solar Cells: Innovations like perovskites, organic solar cells, and quantum dots are making solar technology more affordable and efficient.
- Solar Grid Integration: Solar power can be integrated into the electric grid using inverters, battery storage, and net metering systems.
- Advantages of Solar Energy: Solar power is renewable, reduces electricity bills, and creates jobs while having minimal environmental impact.
Introduction to Solar Photovoltaic Technology
The demand for clean, renewable energy has never been higher, with global awareness about climate change, environmental sustainability, and energy security at an all-time high. Solar energy, particularly photovoltaic (PV) technology, has emerged as one of the most viable and cost-effective solutions. Solar PV systems convert sunlight into electricity, a process that has become an essential part of the global transition to sustainable energy.

In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the basics of solar photovoltaic technology, how it works, its types, the latest advancements in the field, and its potential future. We will also answer some of the most frequently asked questions (FAQs) about solar energy.
Read This Also: Introduction to Solar Energy and How It Works
What is Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Technology and How Does it Work?
At its core, photovoltaic technology refers to the process of converting light energy, or photons, into electrical energy through a semiconductor material, often silicon. This process, known as the photovoltaic effect, was first demonstrated in 1954 by researchers at Bell Laboratories, who successfully created the first working solar cell.
A solar cell is made up of semiconductor materials, usually silicon, that absorb sunlight. When sunlight strikes the cell, the photons (the particles of sunlight) interact with the atoms in the semiconductor material, dislodging electrons. These electrons are then forced to move in a particular direction, creating an electric current.
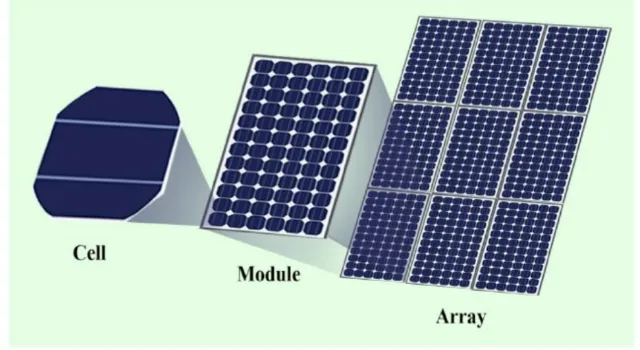
Photovoltaic cells, on their own, are typically small and generate about 1 to 2 watts of electricity. However, to produce more power, these cells are connected to form solar panels or modules. Multiple panels can be linked together to form solar arrays, which can produce significant amounts of electricity.
Types of Solar Photovoltaic Technology
Over the years, PV technology has evolved, and today, we have various types of solar cells, each with its own advantages and specific use cases. Let’s take a deeper look into the three main categories of PV technology: silicon-based cells, thin-film cells, and III-V solar cells.
Silicon Solar Cells: The Standard for Photovoltaics
The most widely used solar cells are made from silicon, the second most abundant element on Earth. Silicon solar cells are relatively cost-effective and offer a balanced efficiency-to-cost ratio. These cells are generally divided into three categories based on their construction:
- Monocrystalline: Made from a single continuous crystal structure, they offer the highest efficiency (typically around 20-22%) and are usually black.
- Polycrystalline: Made from silicon crystals that are melted together, these are generally less efficient (around 15-17%) but cheaper.
- Amorphous: Thin, flexible, and lightweight, these cells are often used for portable solar applications and small-scale power needs but are less efficient.
Silicon solar panels are commonly used for residential solar installations and utility-scale solar farms. Their durability and reliability make them the go-to option for most solar power systems today.
Thin-Film Solar Cells: Flexibility and Lightness
Unlike traditional silicon solar cells, thin-film solar cells are made by depositing semiconductor materials like cadmium telluride or copper indium gallium diselenide (CIGS) onto a substrate, typically glass or plastic. These cells are incredibly thin—often just a few micrometers in thickness—and offer several benefits:
- Lightweight and Flexible: Thin-film solar cells can be integrated into a variety of surfaces, such as windows, roofs, and portable devices, making them versatile.
- Lower Production Costs: They can be manufactured more efficiently and with less energy than silicon-based cells.
However, the efficiency of thin-film solar cells is generally lower, ranging from 10% to 13%. These cells are ideal for large-scale installations, particularly when flexibility and low cost are more important than efficiency.
III-V Solar Cells: High Efficiency for Niche Applications
The III-V solar cells are made from a combination of elements from Group III (gallium, indium) and Group V (arsenic, antimony) of the periodic table. These cells achieve significantly higher efficiency levels, often exceeding 30% or more, but they come at a high manufacturing cost.
These cells are mostly used in specialized applications like space satellites and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), where the high power-to-weight ratio and efficiency of the solar cells outweigh the cost. While not typically used for residential applications, III-V solar cells represent a key area of research for the next generation of solar technologies.
Read This Also: 3 Basic Types of Solar Panels: Monocrystalline, Polycrystalline & Thin-Film
Next-Generation Solar Cells: Innovations on the Horizon
The future of solar photovoltaic technology lies in the next-generation solar cells, including those made from organic materials, quantum dots, and perovskites. Researchers are exploring these materials due to their potential for lower costs and greater efficiency.
Perovskite Solar Cells
Perovskites are a group of materials with a specific crystal structure that has shown remarkable promise in photovoltaic applications. Some perovskite solar cells have achieved efficiency rates exceeding 25%, which is comparable to or even surpasses traditional silicon solar cells. These materials are easier to produce and cost less than silicon, which makes them a potential game-changer for the solar industry.
Organic Solar Cells
Organic solar cells are made from carbon-based materials. While they are still in the experimental phase, organic cells offer a unique advantage in terms of flexibility and low-cost production. If research progresses, organic solar cells could be used in applications such as wearable solar devices or solar-powered textiles.
Quantum Dot Solar Cells
Quantum dots are nanometer-sized semiconductor particles that can absorb light at a range of wavelengths. The efficiency of quantum dot solar cells can be enhanced by controlling the size and shape of the quantum dots, leading to better performance. Researchers are optimistic that these cells could outperform traditional solar cells soon.

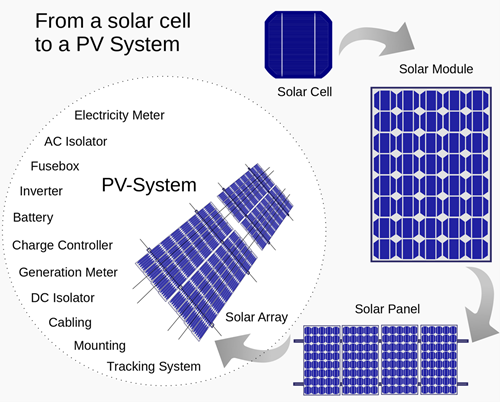
How Solar PV Systems Integrate into the Grid
The growing adoption of solar PV systems has led to significant advancements in grid integration technology. Solar energy is intermittent, meaning it is only generated during daylight hours, and its output can fluctuate due to weather conditions. To ensure reliability, solar PV systems must be paired with energy storage solutions and connected to the smart grid.
- Inverters: Solar PV systems generate direct current (DC) electricity, but the electric grid operates on alternating current (AC). Inverters convert DC to AC, enabling the power to flow into the grid or directly to homes and businesses.
- Battery Storage: To ensure a consistent power supply, energy storage systems, such as lithium-ion batteries, are increasingly used to store excess energy produced during sunny periods for later use when sunlight is unavailable.
- Net Metering: Many regions offer net metering policies, which allow homeowners with solar panels to sell excess electricity back to the grid, providing them with credits that reduce their electricity bills.
Advantages of Solar Photovoltaic Technology
- Renewable Energy Source: Solar power is an infinite and clean source of energy, producing no emissions during operation.
- Low Operating Costs: Once installed, solar PV systems have minimal operating and maintenance costs.
- Grid Independence: Solar panels provide electricity in areas where there is no connection to the electrical grid, such as remote regions or off-grid homes.
- Job Creation: The solar industry has created thousands of jobs globally in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance.
- Government Incentives: Various government policies, including tax incentives and subsidies, make solar energy more affordable for residential and commercial users.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How efficient are solar panels today?
Modern solar panels, particularly monocrystalline silicon panels, have an efficiency of about 20-22%. Some of the latest research has achieved efficiencies of 25% or more, with experimental cells reaching nearly 50% efficiency.
2. Can solar power work on cloudy days?
Yes, solar panels can still produce electricity on cloudy days, although their efficiency may be reduced. Solar panels work best in direct sunlight, but even diffuse light from overcast skies can generate power.
3. What is the lifespan of solar panels?
The average lifespan of solar panels is between 25 and 30 years, with some systems lasting longer with proper maintenance.
4. Do solar panels require maintenance?
Solar panels require very little maintenance. Periodic cleaning and inspections are recommended to ensure optimal performance.
5. How much do solar panels cost?
The cost of solar panels varies depending on the system size, efficiency, and location. On average, the cost of installing solar panels ranges from $10,000 to $30,000 before incentives.
Conclusion
Solar photovoltaic technology has evolved significantly since its inception in the 1950s. With advancements in efficiency, lower costs, and innovations in materials like perovskites and quantum dots, solar power is set to play a central role in meeting the world’s energy needs. As governments, businesses, and homeowners increasingly turn to solar energy, the future of this clean and renewable resource looks brighter than ever.
References:
https://www2.nrel.gov/research/re-photovoltaics
https://www.eia.gov/energyexplained/solar/photovoltaics-and-electricity.php
https://www.energy.gov/eere/solar/solar-photovoltaic-technology-basics


